Lately I was working on a Web Security Project and I came across this very interesting Web Messaging Encryption Protocol - Signal Protocol.
When doing web communication encryption, the most common solution is using TLS, where basically, two sides handshake using Diffie–Hellman key exchange through an insecure channel and communicate using symmetric encryption (i.e.: AES) based on the secret key SK derivated from DH key exchange. This solution can provide strong enough encryption when communicating between client and server.
However, when it comes to the situation where client talks to client (E2E) and server just redirects message, especially instant messaging, there are two major security issues we need to solve:
-
The server itself may be not secure and we are unable to trust it to store the messages in clear or weak encryption;
-
If always relying on the same
SK, this gives Mallory time to crack it out and every message would be able to be decrypted.
To achieve secure E2E communications, the signal protocol was thus introduced. It has two main fragments:
-
Extended Triple Diffie-Hellman(X3DH): This extended DH key exchange helps two clients establish a shared
SKfor future communications in an asynchronous way, only requiring two clients publish some keys to server; -
Double Ratchet algorithm: This algorithm provides both forward secrecy and break-in recovery, which makes each message have different
SKso there is no way to crack oneSKand know everything.
The specifications from Signal Protocol provide a relatively high level overview but there are still some details not that clear and hard to understand. So I would like to talk about how I understand this protocol with some actual implementation in Python. In this post, I will focus on the X3DH part.
X3DH Protocol
How shared DH Value computed in X3DH is using X25519 Key exchange which is a Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman. And I chose library cryptography, which is part of pyOpenSSL, to compute this X25519 Key exchange.
The basic workflow of establishing a session using X3DH is illustrated as below:
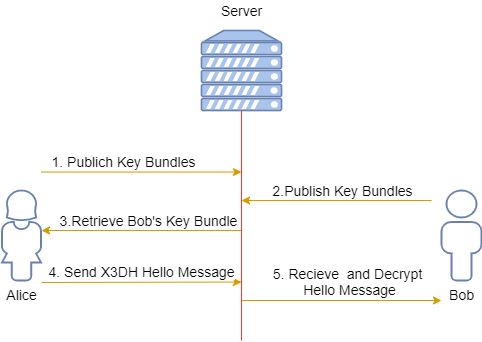
Preparation
At first, both clients need to generate required key pairs, publish key bundles to server and save the secrets so they are able to start the session.
Key pairs to generate:
-
IK: Long-Term Identity Key (32 bytes both), which is an unique identifier for each client; -
SPK: Signed PreKey (32 bytes both), a key pair will be revoked and re-generated every few days/weeks for sake of security. Alongside,SPK_sig:SPKpublic key’s signature, signed byIKsecret key -SIG(IK_s, SPK_p); -
OPK: One-time Off Key (32 bytes both), a key pair will be revoked once used for handshake. Usually, the client will generate multipleOPKpair and generate new one once server used up or needs more.
Then all these key pair’s public keys and SPK_sig will be sent to server.
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import x25519
from XEdDSA import sign
class User():
def __init__(self, name, MAX_OPK_NUM):
self.name = name
self.IK_s = x25519.X25519PrivateKey.generate()
self.IK_p = self.IK_s.public_key()
self.SPK_s = x25519.X25519PrivateKey.generate()
self.SPK_p = self.IK_s.public_key()
self.SPK_sig = sign(IK_s, SPK_p)
self.OKPs = []
self.OPKs_p = []
for i in range(MAX_OPK_NUM):
sk = x25519.X25519PrivateKey.generate()
pk = sk.public_key()
self.OPKs_p.append(pk)
self.OKPs.append((sk, pk))
# for later steps
self.key_bundles = {}
self.dr_keys= {}
def publish(self):
return {
'IK_p': self.IK_p,
'SPK_p': self.SPK_p,
'SPK_sig': self.SPK_sig,
'OPKs_p': self.OPKs_p
}
Due to unable to find out how to do XEdDSA signature required by signal protocol while using cryptography, since each library has their different way to format their X25519 Keys, here I picked a mock function sign. You could refer to this blog post and RFC Standard to convert between Ed25519 and X25519
Establish the Session
To actually establish the session, steps 3-5 in the diagram above will be carried out by Alice and Bob.
- First, Alice tries to send first message. Her client will ask server for Bob’s key bundle and generate a Ephemeral Key pair use only for this handshake:
# Continue in Class Client
# Get key bundle from a server object
def get_key_bundle(self, server, user_name):
if user_name in self.key_bundles and user_name in self.dr_keys:
print('Already stored ' + user_name + ' locally, no need handshake again')
return False
self.key_bundles[user_name] = server.get_key_bundle(user_name)
return True
def initial_handshake(self, server, user_name):
if get_key_bundle(user_name):
# Generate Ephemeral Key
sk = x25519.X25519PrivateKey.generate()
self.key_bundles[user_name]['EK_s'] = sk
self.key_bundles[user_name]['EK_p'] = sk.public_key()
return
-
Then, Alice’s client will compute Alice’s secret key
SK, with-
IK_saAlice’s secret Identity key, -
EK_pkAlice’s public Ephemeral Key, -
IK_pbBob’s public Identity Key, -
SPK_pbBob’s public Signed PreKey, -
OPK_pbBob’s public One-time Off key
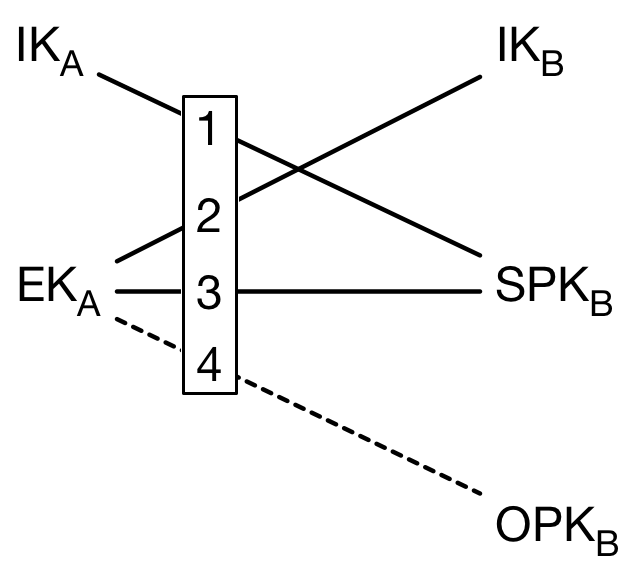
getting 4
DHvalues and derivate a 32 bytesSK, whereSK = HKDF(DH_1||DH_2||DH_3||DH_4)from Crypto.Protocol.KDF import HKDF from Crypto.Hash import SHA256 from XEdDSA import verify KDF_F = b'\xff' * 32 KDF_LEN = 32 KDF_SALT = b'\0' * KDF_LEN # Continue in Class Client def x3dh_KDF(key_material): km = KDF_F + key_material return HKDF(km, KDF_LEN, KDF_SALT, SHA256, 1) def generate_send_secret_key(self, user_name): key_bundle = self.key_bundles[user_name] DH_1 = self.IK_s.exchange(key_bundle['SPK_p']) DH_2 = key_bundle['EK_s'].exchange(key_bundle['IK_p']) DH_3 = key_bundle['EK_s'].exchange(key_bundle['SPK_p']) DH_4 = key_bundle['EK_s'].exchange(key_bundle['OPK_p']) if not verify(self.IK_s, key_bundle['SPK_sig']): print('Unable to verify Signed Prekey') return # create SK key_bundle['SK'] = x3dh_KDF(DH_1 + DH_2 + DH_3 + DH_4)The
HKDFhere I pick is from pycryptodome. And note that X3DH requiresHKDFfunction prepend 32b'\xff'bytes if curve is X25519, and 57b'\xff'bytes if curve is X448. The salt should ab'\0'byte sequence of length equals to length of output key length. Hash functions are required to be a 256-bit or 512-bit function. -
-
Then, Alice’s client will build the hello message to send out:
The format of the initial message:
IK_pb||EK_pa||OPK_pb||n_0||t_0||AES(SK, SIG(IK_sa, IK_pa||EK_pa||OPK_pb||AD)||IK_pa||IK_pb||AD)and you could set the
AD’s format like this:{ "from": "alice", "to": "bob", "message": "<some greeting messages>" }Implement in Python:
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization from Crypto.Random import get_random_bytes from Crypto.Cipher import AES import json # Length definition for hello message encryption AES_N_LEN = 16 AES_TAG_LEN =16 # Continue in Class Client def dump_privatekey(private_key, to_str=True): private_key = private_key.private_bytes( encoding=serialization.Encoding.Raw, format=serialization.PrivateFormat.Raw, encryption_algorithm=serialization.NoEncryption() ) return private_key def dump_publickey(public_key): public_key = public_key.public_bytes( encoding=serialization.Encoding.Raw, format=serialization.PublicFormat.Raw ) return public_key def build_x3dh_hello(self, server, to, ad): # Binary additional data b_ad = (json.dumps({ 'from': self.name, 'to': to, 'message': ad })).encode('utf-8') key_bundle = self.key_bundles[to] # 64 byte signature key_comb = dump_publickey(self.IK_p) + dump_publickey(key_bundle['EK_p']) +dump_publickey(key_bundle['OPK_p']) signature = sign(self.IK_s, key_comb + b_ad) print("Alice message signature: ", signature) print("data: ", key_comb + b_ad) # 16 byte aes nonce nonce = get_random_bytes(AES_N_LEN) cipher = AES.new(key_bundle['SK'], AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=nonce, mac_len=AES_TAG_LEN) # 32 + 32 + len(ad) byte cipher text ciphertext, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(signature + dump_publickey(self.IK_p) + dump_publickey(key_bundle['IK_p']) + b_ad) # initial message: (32 + 32 +32) + 16 + 16 + 64 + 32 + 32 + len(ad) message = key_comb + nonce + tag + ciphertext server.send(to, message) # For Double Ratchet self.initialize_dr_state(to, key_bundle['SK'], [key_bundle['EK_s'], key_bundle['EK_p']], "")AESrefersAES256in GCM Mode,n_0andt_0are nonce and tag, usingSKas key, which is also from pycryptodome. -
Finally, Bob receives first message, decrypts and verifies it:
Bob will also check out Alice’s key bundle from server and manipulate the hello message to compute his
SK. And then decrypt the message and verify the signature in the plaintext for AEAD.The verifications include:
-
verify public signed PreKey’s signature
SPK_sig; -
verify
IK_pbandOPK_pbin the hello message and in the local db matches; -
verify
IK_pain the hello message and in key bundles matches; -
verify
AD, the json object in the hello message has correct from and to.
EC_KEY_LEN = 32 # Continue in Class Client def recv_x3dh_hello_message(self, server): # receive the hello message sender, recv = server.get_message() self.get_key_bundle(server, sender) key_bundle = self.key_bundles[sender] IK_pa = recv[:EC_KEY_LEN] EK_pa = recv[EC_KEY_LEN:EC_KEY_LEN*2] OPK_pb = recv[EC_KEY_LEN*2:EC_KEY_LEN*3] nonce = recv[EC_KEY_LEN*3:EC_KEY_LEN*3+AES_N_LEN] tag = recv[EC_KEY_LEN*3+AES_N_LEN:EC_KEY_LEN*3+AES_N_LEN+AES_TAG_LEN] ciphertext = recv[EC_KEY_LEN*3+AES_N_LEN+AES_TAG_LEN:] # Verify if the key in hello message matches the key bundles from server if (IK_pa != key_bundle['IK_p']): print("Key in hello message doesn't match key from server") return # Verify Signed pre key from server if not verify(key_bundle['IK_p'], key_bundle['SPK_sig']): print('Unable to verify Signed Prekey') return sk = create_recv_secret_key(IK_pa, EK_pa, OPK_pb) print('bob sk: ', sk) if sk is None: return key_bundle['SK'] = sk message = x3dh_decrypt_and_verify(self, key_bundle, IK_pa, EK_pa, nonce, tag, ciphertext) # For Double Ratchet self.initialize_dr_state(sender, sk, [], EK_pa) # Get Ek_pa and plaintext ad return EK_pa, message def generate_recv_secret_key(self, IK_pa, EK_pa, OPK_pb)): # Find corresponding secret OPK secret key # And remove the pair from the list OPK_sb = self.search_OPK_lst(OPK_pb) if OPK_sb is None: return IK_pa = x25519.X25519PublicKey.from_public_bytes(IK_pa) EK_pa = x25519.X25519PublicKey.from_public_bytes(EK_pa) DH_1 = self.SPK_s.exchange(IK_pa) DH_2 = self.IK_s.exchange(EK_pa) DH_3 = self.SPK_s.exchange(EK_pa) DH_4 = OPK_sb.exchange(EK_pa) # create SK return x3dh_KDF(DH_1 + DH_2 + DH_3 +DH_4) def x3dh_decrypt_and_verify(self, key_bundle, IK_pa, EK_pa, nonce, tag, ciphertext): # Decrypt cipher text and verify cipher = AES.new(decodeB64Str(sk), AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=nonce, mac_len=AES_TAG_LEN) try: p_all = cipher.decrypt_and_verify(ciphertext, tag) except ValueError: print('Unable to verify/decrypt ciphertext') return except Exception as e: print('e') return # Byte format of plain text sign = p_all[:EC_SIGN_LEN] IK_pa_p = p_all[EC_SIGN_LEN:EC_SIGN_LEN+EC_KEY_LEN] IK_pb_p = p_all[EC_SIGN_LEN+EC_KEY_LEN:EC_SIGN_LEN+EC_KEY_LEN*2] ad = p_all[EC_SIGN_LEN+EC_KEY_LEN*2:] if (IK_pa != IK_pa_p and IK_pb != IK_pb_p): print("Keys from header and ciphertext not match") return if not verify(IK_pa], sign, IK_pa_p + EK_pa + OPK_pb + ad): print("Unable to verify the message signature") return print('Message: ', json.loads(ad)) return json.loads(ad) -
Next Step
After both Alice and Bob share a SK, X3DH can be marked as completed. Though this process is hard to be cracked out, we have to integrate it with Double Ratchet Algorithm to reach ultimate secure in application layer (Again, this only encrypts the request/response data but not IP/TCP or others). And I will talk about it in the next part.
For now, we just need to make sure what to keep for DR integration and what to destroy to avoid reuse attack.
Alice, Bob and server need to destroy the OPK from Bob used in this handshake.
Alice needs to keep EK pair and SK to initiate DR.
Bob also needs to keep Alice’s EK_p and SK to initiate DR and send his response using DR.